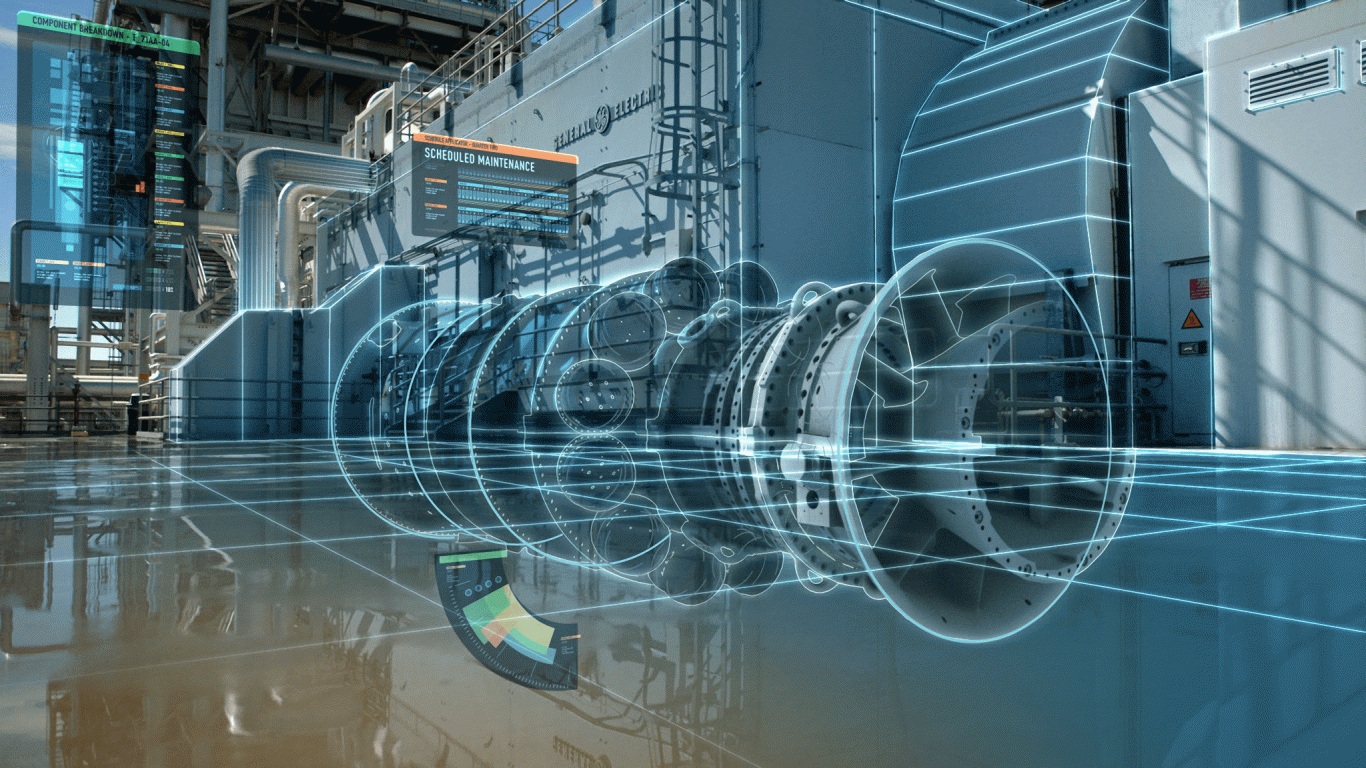
What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a digital representation of a physical object or system. The technology behind digital twins has expanded to include large items such as buildings, factories, and even cities. Some have said people and processes could have digital twins, developing the concept even further. The idea first arose at NASA: full-scale mockups of early space capsules, used on the ground to mirror and diagnose problems in orbit, eventually gave way to fully digital simulations.
But the term took off after Gartner named digital twins as one of its top 10 strategic technology trends for 2017, saying that within three to five years, “billions of things will be represented by digital twins, a dynamic software model of a physical thing or system.” A year later, Gartner once again named digital twins as a top trend, saying that “with an estimated 21 billion connected sensors and endpoints by 2020, digital twins will exist for billions of things soon.”
In essence, a digital twin is a computer program that takes real-world data about a physical object or system as inputs and produces output predictions or simulations of how that physical object or design will be affected by those inputs.
How do Digital twins work?
Digital Twins, the virtual counterparts of the physical assets, are created as digitized duplicates of machines/equipment or physical sites using sensors. These digital assets can be made even before an asset is built physically. To create a digital twin of any physical asset, the engineers collect and synthesize data from various sources, including biological data, manufacturing data, operational data, and analytics software insights. All this information and AI algorithms are reintegrated into a physics-based virtual model. By applying Analytics to these models, we get the relevant insights regarding the physical asset. The consistent flow of data helps get the best possible analysis and insights regarding the asset, optimizing the business outcome. Thus the digital twin will act as a live model of the physical equipment.
Applications of Digital Twins
The Digital Twin concept is the next big thing in most business sectors, which accurately predicts physical assets’ current state and future by analyzing their digital counterparts. By implementing, organizations can gain better insights on product performance, improve customer service, and make better operational and strategic decisions based on these insights.
6 Business Sectors with Digital Twins Applications
Benefits of digital twins with business applications are extremely useful in the following sectors:
- Manufacturing: The area where digital twins rollouts are probably the furthest along, with factories already using digital twins to simulate their processes, as in this case study from Deloitte.
- Automotive: digital twins are made possible because cars are already fitted with telemetry sensors, but refining the technology will become more important as more autonomous vehicles hit the road.
- Healthcare: is the sector that produces the digital twins of people we mentioned above. Band-aid sized sensors send health information back to a digital twin used to monitor and predict a patient’s well-being.
- Retail: Appealing customer experience is key in the retail sector. Digital twin implementation can play a key role in augmenting the retail customer experience by creating virtual twins for customers and modeling fashions. They also help in better in-store planning, security implementation, and energy management in an optimized manner.
- Smart Cities: Smart city planning and implementation with Digital Twins and IoT data help enhance economic development, efficient management of resources, reduce the ecological footprint, and increase the overall quality of a citizen’s life. The digital twin model can help city planners and policymakers in smart city planning by gaining insights from various sensor networks and intelligent systems. The data from the digital twins help them in arriving at informed decisions regarding the future as well.
- Industrial IoT: Industrial firms with digital twin implementation can now monitor, track, and control industrial systems digitally. Apart from the operational data, the digital twins capture environmental data such as location, configuration, financial models, etc., which predicts future operations and anomalies.
Digital twins and IoT
The explosion of IoT sensors is part of what makes digital twins possible. And as IoT devices are refined, digital-twin scenarios can include smaller and less complicated objects, giving additional benefits to companies.
Digital twins can be used to predict different outcomes based on variable data. This is similar to the run-the-simulation scenario often seen in science-fiction films, where a possible scenario is proven within the digital environment. With additional software and data analytics, digital twins can continually optimize an IoT deployment for maximum efficiency and help designers figure out where things should go or how they operate before they are physically deployed.
The more that a digital twin can duplicate the physical object, the more likely efficiencies and other benefits can be found. For instance, in manufacturing, where the more highly instrumented devices are, the more accurately digital twins might simulate how the tools have performed over time, which could help predict future performance and possible failure.
Digital twins in the industry 4.0
The fourth industrial revolution or Industry 4.0 embraces automation, data exchange, and manufacturing technologies as the business world’s talking point. Digital Twins is at the core of this new industrial revolution bringing in unlimited possibilities. It changes the traditional approach of ‘the first build and then tweak’ in the industrial world and brings in a more virtual system based design process that brings in a much more efficient role out of any equipment or system by understanding its unique features, performance, and potential issues if any. With Digital Twin, an operator can train a virtual machine without spending on a dedicated trainer or simulator. With the further evolution of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, the future is not too far for machines to take autonomy to the next level. In such an autonomous world of industrial machines, Digital Twin’s role will evolve, and we can witness increasing self-awareness in the machines. Such devices will be capable of optimizing their performance, coordinating with other machines, doing self-diagnosis, and self-repairing the faults, if any, with minimal intervention from a manual operator. No doubt, there is an exciting future to get unfold in the world of Manufacturing and Engineering, and Digital Twins is a significant step to it. To unlock this vast potential, are you ready?
Benefits of Digital twins
Digital twins offer a real-time look at what’s happening with physical assets, which can radically alleviate maintenance burdens. Chevron is rolling out digital twin tech for its oil fields and refineries and expects to save millions of dollars in maintenance costs. As part of its pitch, Siemens says that using digital twins to model and prototype objects that have not been manufactured can reduce product defects and shorten time to market.
But keep in mind that Gartner warns that digital twins aren’t always called for and can unnecessarily increase complexity. Digital twins could be technology overkill for a particular business problem. There are also concerns about cost, security, privacy, and integration.”
Five Benefits of Digital twins
- Extend the life of assets and equipment
- Uncover operational inefficiencies
- Help deploy preventive maintenance, reduce maintenance costs.
- Enable better response to episodes of downtime
- Improve situational awareness


Great article. I would argue that digital twins are also highly valuable in facilities management – creating a digital replica of the building from 3D scans and sensors would enable FMs to reduce operational costs, plan remodelling works, and more.
Thank you so much for this article! This was exactly what I needed.